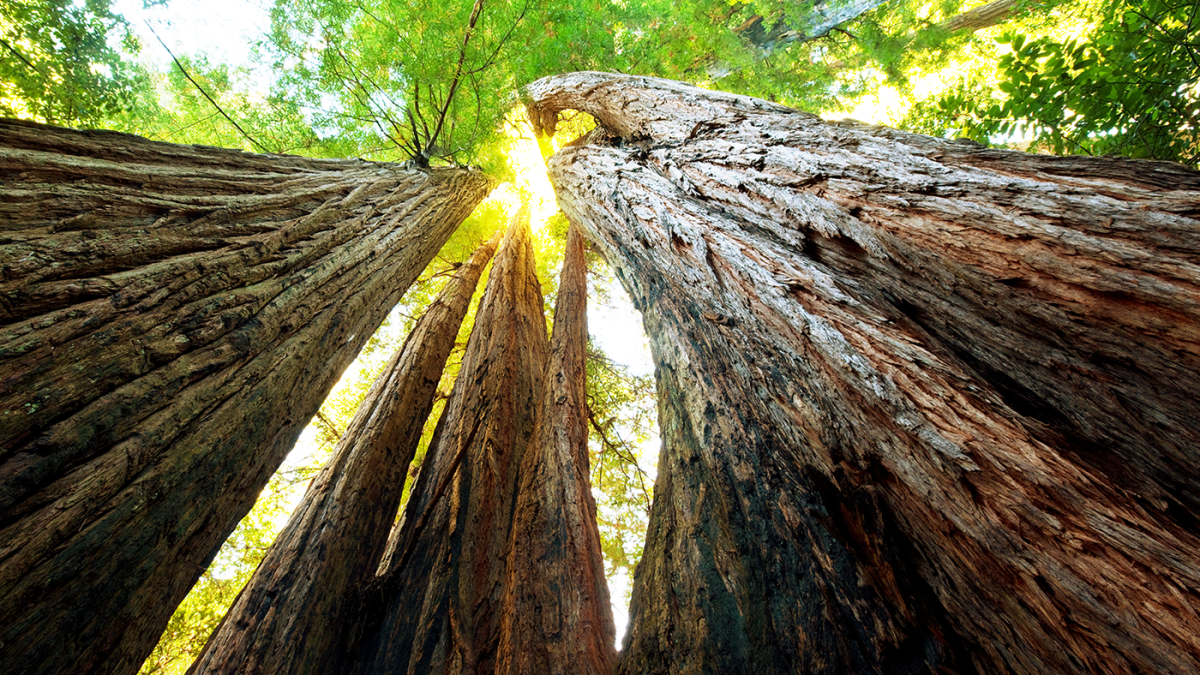
Redwoods, some of the tallest and most ancient trees on Earth, are a symbol of nature's grandeur and resilience. These towering giants can be found in specific regions of the world, primarily along the coast of California and parts of the Pacific Northwest. Their presence is a testament to the delicate balance between nature and human activity, making them an essential focus for conservation efforts.
For centuries, redwoods have fascinated scientists, nature enthusiasts, and travelers alike. Their immense size and longevity make them a natural wonder that continues to inspire awe. These trees are not only vital to the ecosystems they inhabit but also serve as a reminder of the importance of preserving our planet's biodiversity.
As we delve into the world of redwoods, we will explore their habitats, ecological significance, and the challenges they face in today's rapidly changing environment. Whether you're a nature lover, an environmentalist, or simply curious about these majestic trees, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of where redwoods are located and why they matter.
Read also:Rothman Institute Elevating The Game For Philadelphia Eagles
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Redwoods
- Where Are Redwoods Naturally Found?
- Types of Redwoods: Coastal and Giant
- The Role of Redwoods in Their Ecosystem
- Threats to Redwoods and Conservation Efforts
- Climate Conditions for Redwood Growth
- Redwoods and Tourism: Exploring the Giants
- Scientific Research on Redwoods
- Historical Significance of Redwoods
- Future Prospects for Redwoods
Introduction to Redwoods
Redwoods are among the most iconic trees in the world, known for their towering height and incredible lifespan. These trees belong to the Sequoioideae subfamily and are divided into two primary species: Sequoia sempervirens (coast redwoods) and Sequoiadendron giganteum (giant sequoias). Both species are native to California, but they thrive in different environments and play distinct roles in their respective ecosystems.
Why Are Redwoods Important?
Redwoods are not just visually stunning; they also play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Their towering canopies provide habitat for countless species, while their roots help prevent soil erosion and maintain water quality. Additionally, redwoods are carbon sequestration powerhouses, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping mitigate climate change.
Understanding where redwoods are located and the conditions they require to thrive is essential for preserving these natural wonders for future generations.
Where Are Redwoods Naturally Found?
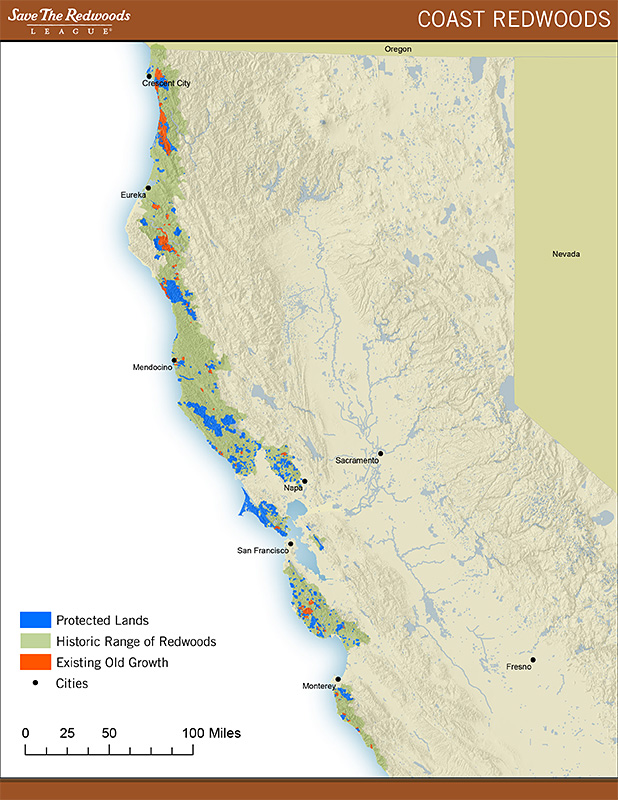
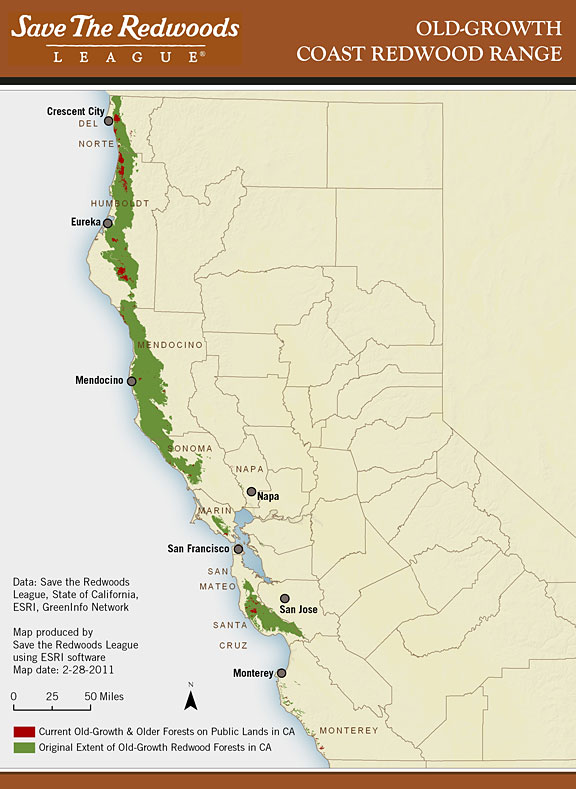
Redwoods are native to specific regions along the western coast of the United States, primarily in California and parts of Oregon. The coastal redwoods (Sequoia sempervirens) thrive in the foggy coastal regions of Northern California, while giant sequoias (Sequoiadendron giganteum) are found in the Sierra Nevada mountain range.
Coastal Redwood Distribution
Coastal redwoods are predominantly found in a narrow strip along the Pacific Coast, stretching from the southern border of Oregon to the Big Sur region in California. This area is characterized by a cool, moist climate, which is ideal for redwood growth. The frequent fog in these regions provides the necessary moisture for the trees to survive, even during dry summer months.
Giant Sequoia Distribution
Giant sequoias, on the other hand, are restricted to the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada. These trees require a specific combination of elevation, soil type, and precipitation to thrive. Unlike coastal redwoods, giant sequoias are not dependent on coastal fog but rely on snowmelt from the mountains for their water needs.
Read also:Gabi Garcia Nude The Truth Behind The Headlines And Sensationalism
Types of Redwoods: Coastal and Giant
There are two main types of redwoods, each with unique characteristics and habitats:
- Coast Redwoods: Known for their incredible height, coast redwoods can grow up to 379 feet (115 meters) tall. They are the tallest trees on Earth and are found primarily along the Pacific Coast.
- Giant Sequoias: While not as tall as coast redwoods, giant sequoias are the largest trees by volume. They can reach heights of up to 300 feet (91 meters) and have massive trunks that can exceed 30 feet (9 meters) in diameter.
Key Differences Between the Two Species
Although both species are classified as redwoods, they differ significantly in terms of size, habitat, and growth patterns. Coastal redwoods are adapted to the moist coastal climate, while giant sequoias thrive in the drier, higher-elevation environments of the Sierra Nevada.
The Role of Redwoods in Their Ecosystem
Redwoods play a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of their ecosystems. Their towering canopies provide shade and habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species. The forest floor beneath redwoods is rich in organic matter, which supports diverse microbial communities and contributes to soil fertility.
Biodiversity in Redwood Forests
Redwood forests are home to numerous species of plants and animals, many of which are found nowhere else in the world. The dense canopy of redwoods creates a microclimate that supports a wide range of life forms, from ferns and fungi to birds and mammals. Some of the key species found in redwood forests include:
- Marbled murrelets
- Spotted owls
- California red-legged frogs
- Coastal tailed frogs
Threats to Redwoods and Conservation Efforts
Despite their resilience, redwoods face numerous threats, including logging, urban development, climate change, and disease. Historically, extensive logging has led to the destruction of many old-growth redwood forests, leaving only a fraction of their original range intact.
Conservation Initiatives
To protect these magnificent trees, various conservation organizations and government agencies have implemented programs aimed at preserving redwood habitats. National parks such as Redwood National and State Parks and Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks have been established to safeguard these ecosystems. Additionally, efforts to restore degraded forests and promote sustainable forestry practices are underway.
Climate Conditions for Redwood Growth
Redwoods require specific climate conditions to thrive. Coastal redwoods, for example, depend on the frequent fog that rolls in from the Pacific Ocean to provide moisture during the dry summer months. This fog drip is essential for maintaining soil moisture and supporting the trees' growth.
Impact of Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to redwoods, as it alters the patterns of precipitation and temperature that these trees rely on. Rising temperatures and reduced fog frequency could make it more challenging for redwoods to survive in their traditional habitats, necessitating new conservation strategies to ensure their survival.
Redwoods and Tourism: Exploring the Giants
Redwood forests are popular destinations for tourists and nature enthusiasts from around the world. The towering trees and lush surroundings offer a unique and unforgettable experience for visitors. Many national and state parks provide opportunities for hiking, camping, and wildlife viewing in these majestic forests.
Popular Redwood Parks
Some of the most popular redwood parks include:
- Redwood National and State Parks
- Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks
- Julia P. McDonald State Park
- Montgomery Woods State Natural Reserve
Scientific Research on Redwoods
Scientists continue to study redwoods to better understand their biology, ecology, and responses to environmental changes. Research focuses on topics such as tree growth patterns, carbon sequestration capabilities, and the effects of climate change on redwood populations.
Key Findings
Recent studies have revealed that redwoods are among the most efficient carbon sinks on the planet, capable of storing vast amounts of carbon in their massive trunks and roots. This makes them a valuable asset in the fight against climate change.
Historical Significance of Redwoods
Redwoods have played an important role in the history and culture of the regions where they are found. Native American tribes such as the Yurok and Hupa have long revered these trees for their spiritual significance and practical uses. European settlers were similarly captivated by the redwoods, though their initial interactions often involved exploitation rather than preservation.
Cultural Importance
Today, redwoods are celebrated as symbols of strength, resilience, and natural beauty. They serve as a reminder of the importance of protecting our planet's natural resources and preserving the biodiversity that sustains life on Earth.
Future Prospects for Redwoods
The future of redwoods depends on continued efforts to protect their habitats and address the challenges posed by climate change. Advances in conservation science and technology, along with increased public awareness, offer hope for the long-term survival of these magnificent trees.
By supporting conservation organizations, advocating for sustainable practices, and educating others about the importance of redwoods, we can ensure that these natural wonders continue to inspire and awe generations to come.
Conclusion
Redwoods are an extraordinary example of nature's grandeur and resilience. From their towering heights to their vital role in maintaining ecological balance, these trees are a testament to the beauty and complexity of the natural world. Understanding where redwoods are located and the conditions they require to thrive is essential for preserving these majestic giants for future generations.
We encourage you to explore the world of redwoods further, whether through visiting one of the many national parks that protect these trees or by supporting conservation efforts. Share this article with others and help spread awareness about the importance of preserving our planet's natural treasures. Together, we can make a difference in ensuring that redwoods continue to inspire and amaze for centuries to come.