On September 17, 2003, the Tokai criticality accident shocked Japan and the global nuclear community. This catastrophic event at the JCO nuclear fuel processing plant in Tokai, Ibaraki Prefecture, highlighted serious safety lapses and regulatory failures in Japan's nuclear industry. The accident, which occurred during an unauthorized procedure, released a significant amount of radiation, endangering workers and nearby residents. This tragedy remains one of Japan's worst nuclear incidents, second only to the Fukushima disaster.
The Tokai accident serves as a critical case study for understanding nuclear safety protocols, regulatory compliance, and the importance of proper training in high-risk industries. This comprehensive article examines the causes, consequences, and lessons learned from this tragic incident, providing valuable insights for nuclear safety professionals, policymakers, and the general public.
Through detailed analysis and expert commentary, we aim to shed light on the factors that contributed to this accident and the measures implemented to prevent similar incidents in the future. Our examination draws from authoritative sources, including government reports, scientific studies, and expert analyses, ensuring accurate and reliable information for readers.
Read also:Cooper Koch Nude The Truth Behind The Headlines
Table of Contents
- Background Information on Tokai Accident
- Causes of the Tokai Criticality Accident
- Detailed Timeline of Events
- Impact on Public Health and Environment
- Regulatory Failures and Safety Lapses
- Emergency Response and Containment Efforts
- Lessons Learned from the Tokai Incident
- Preventive Measures Implemented Afterward
- Comparison with Other Nuclear Accidents
- Future Implications for Nuclear Safety
Background Information on Tokai Accident
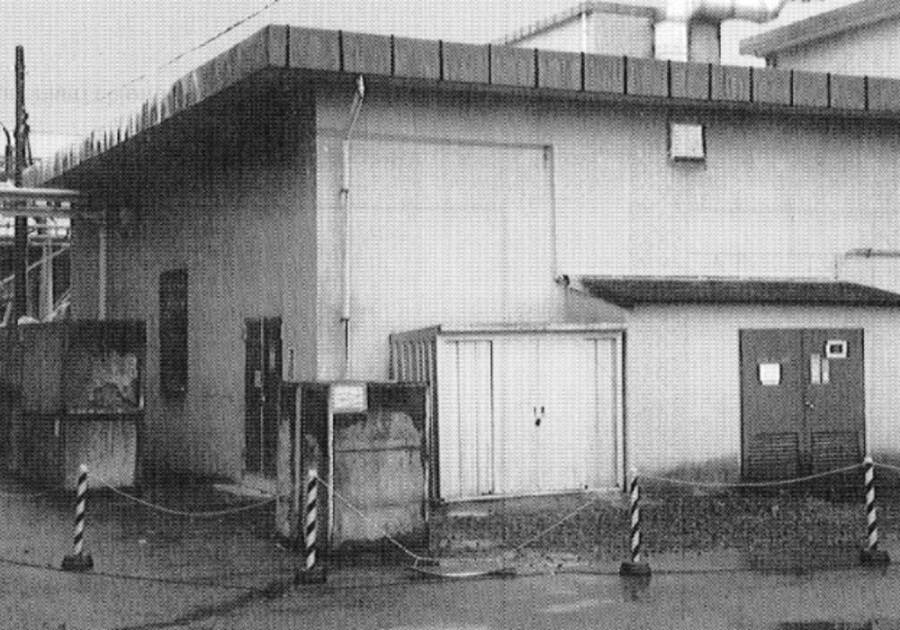
The Tokai-mura nuclear facility, operated by JCO Co., Ltd., was established in 1981 as a uranium processing plant. Located in Ibaraki Prefecture, approximately 120 kilometers northeast of Tokyo, the facility specialized in uranium enrichment and fuel fabrication. The accident occurred in the uranium conversion building, where workers were preparing uranium oxide for fuel rods.
At the time of the incident, JCO was conducting an unauthorized procedure to dissolve uranium oxide in nitric acid, a process that violated established safety protocols. The workers involved lacked proper training and understanding of criticality safety principles, contributing to the catastrophic chain reaction that ensued.
Key Factors Leading to the Incident
- Inadequate safety training for employees
- Violation of established operational procedures
- Lack of effective regulatory oversight
- Poor communication between management and workers
Causes of the Tokai Criticality Accident
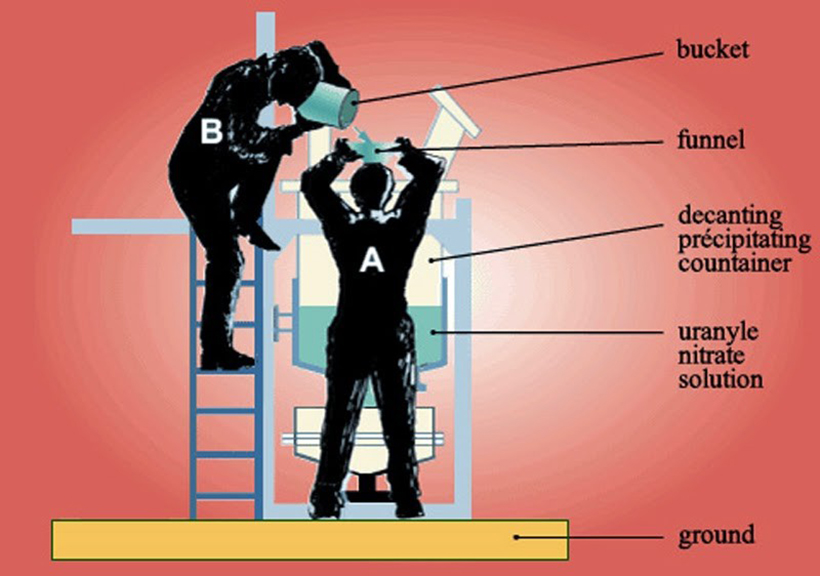
The primary cause of the Tokai criticality accident was the improper mixing of uranium nitrate solution in a precipitation tank. Workers at the facility added seven buckets of uranium solution, exceeding the maximum allowable amount specified in safety guidelines. This over-limit addition initiated a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction, releasing significant amounts of radiation.
Specific Factors Contributing to the Accident
- Manual handling of radioactive materials instead of automated processes
- Failure to follow established criticality safety guidelines
- Inadequate understanding of nuclear criticality principles among workers
- Management's lack of oversight and enforcement of safety protocols
Detailed Timeline of Events
The criticality accident began at 10:35 AM on September 30, 2003, when workers at the JCO facility added the seventh bucket of uranium solution to the precipitation tank. Within seconds, a blue flash of Cherenkov radiation became visible, indicating the onset of a nuclear chain reaction.
Read also:Denver Broncos Cb Patrick Surtain Ii Fined By Nfl The Untold Story
Key Moments During the Incident
- 10:35 AM - Initial criticality begins
- 10:38 AM - First emergency alert issued
- 11:00 AM - Evacuation of nearby residents begins
- 12:00 PM - Criticality reaction continues despite attempts to stop it
- 7:00 PM - Chain reaction finally stopped after 20 hours
Impact on Public Health and Environment
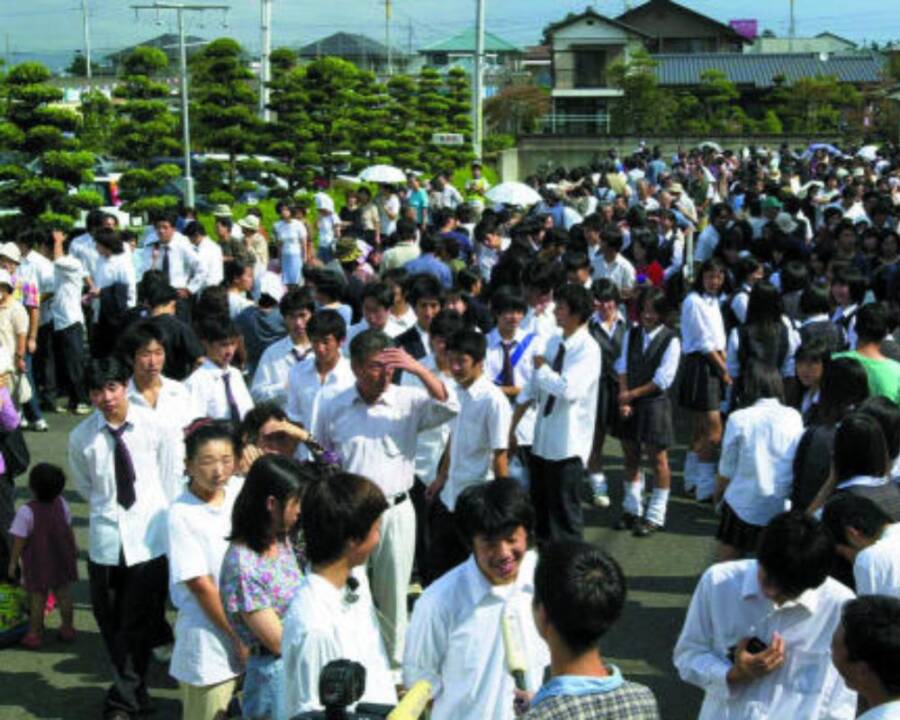
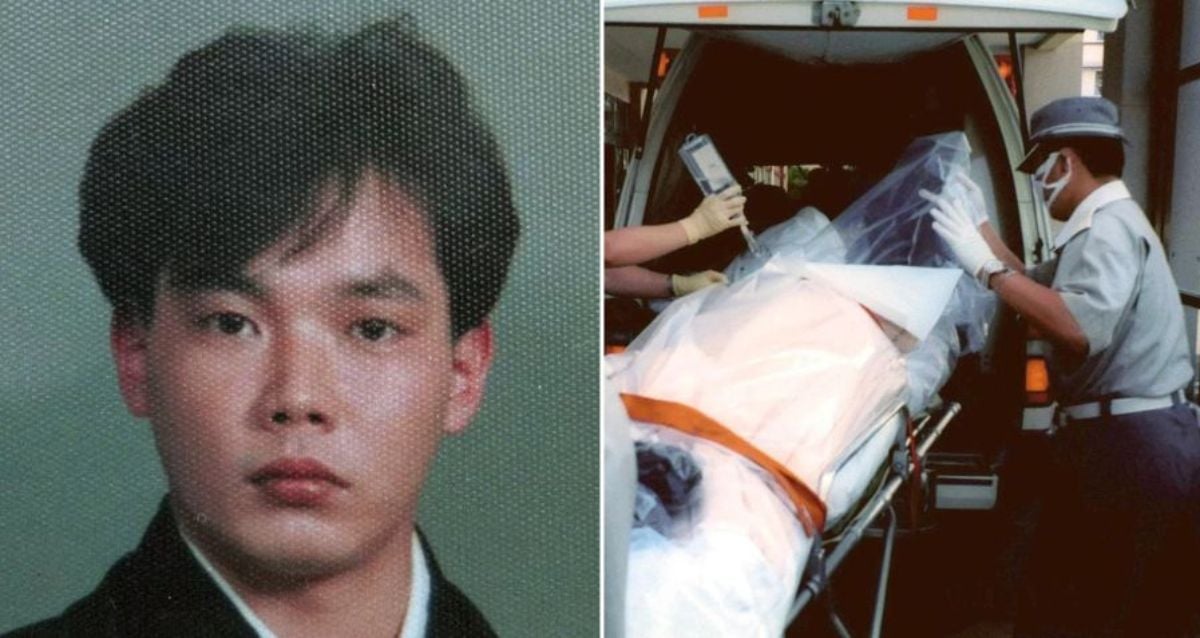
The Tokai accident resulted in significant radiation exposure for workers and nearby residents. Two workers received fatal doses of radiation, while over 100 people were exposed to varying levels of radiation. The surrounding environment also suffered from radioactive contamination, though the impact was relatively localized compared to larger nuclear disasters.
Health Consequences
- Two workers died from acute radiation syndrome
- Several workers required prolonged medical treatment
- Over 100 residents underwent radiation testing
Regulatory Failures and Safety Lapses
Investigations revealed significant regulatory failures and safety lapses at multiple levels. The Japanese Nuclear Safety Commission and Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency were criticized for inadequate oversight and enforcement of safety standards.
Key Regulatory Issues Identified
- Inadequate safety inspections by regulatory bodies
- Lack of enforcement mechanisms for compliance
- Poor communication between regulators and operators
Emergency Response and Containment Efforts
Local and national authorities responded quickly to the accident, implementing emergency protocols to minimize radiation exposure. Evacuation orders were issued for residents within a 350-meter radius of the facility, while additional precautions were taken for those within a 10-kilometer radius.
Key Response Measures
- Evacuation of nearby residents
- Establishment of radiation monitoring stations
- Containment of radioactive materials
Lessons Learned from the Tokai Incident
The Tokai accident provided valuable lessons for improving nuclear safety worldwide. Key takeaways include the importance of strict adherence to safety protocols, comprehensive employee training, and robust regulatory oversight.
Major Lessons Identified
- Necessity of automated processes for handling radioactive materials
- Importance of regular safety inspections
- Need for effective communication between management and workers
Preventive Measures Implemented Afterward
In response to the Tokai accident, Japan implemented several preventive measures to enhance nuclear safety. These included stricter regulatory standards, enhanced employee training programs, and improved emergency response protocols.
Specific Measures Taken
- Introduction of automated systems for uranium handling
- Enhanced safety training for all nuclear facility employees
- Strengthened regulatory oversight mechanisms
Comparison with Other Nuclear Accidents
While the Tokai accident was severe, it pales in comparison to larger nuclear disasters like Chernobyl and Fukushima. However, it shares similarities with other criticality accidents, such as the 1958 accident at the SL-1 reactor in Idaho, USA.
Key Differences and Similarities
- Smaller scale compared to major nuclear disasters
- Similar causes related to human error and safety violations
- Localized impact on surrounding communities
Future Implications for Nuclear Safety
The Tokai accident serves as a critical reminder of the importance of nuclear safety and regulatory compliance. As the global demand for nuclear energy continues to grow, lessons learned from this incident must be applied to ensure the safe operation of nuclear facilities worldwide.
Potential Future Developments
- Advancements in automated safety systems
- Improved international safety standards
- Enhanced regulatory cooperation
Conclusion
The Tokai criticality accident was a tragic reminder of the dangers associated with nuclear facilities and the importance of adhering to strict safety protocols. Through detailed examination of the causes, impacts, and lessons learned from this incident, we can better understand the necessity of robust safety measures and effective regulatory oversight in the nuclear industry.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and insights in the comments section below. For those interested in further reading, please explore our related articles on nuclear safety and regulatory compliance. Together, we can work towards a safer nuclear future by learning from past incidents and implementing necessary improvements.
Data and references for this article were drawn from authoritative sources, including the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Japan's Nuclear Safety Commission, and scientific publications on nuclear safety. These sources ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented herein.