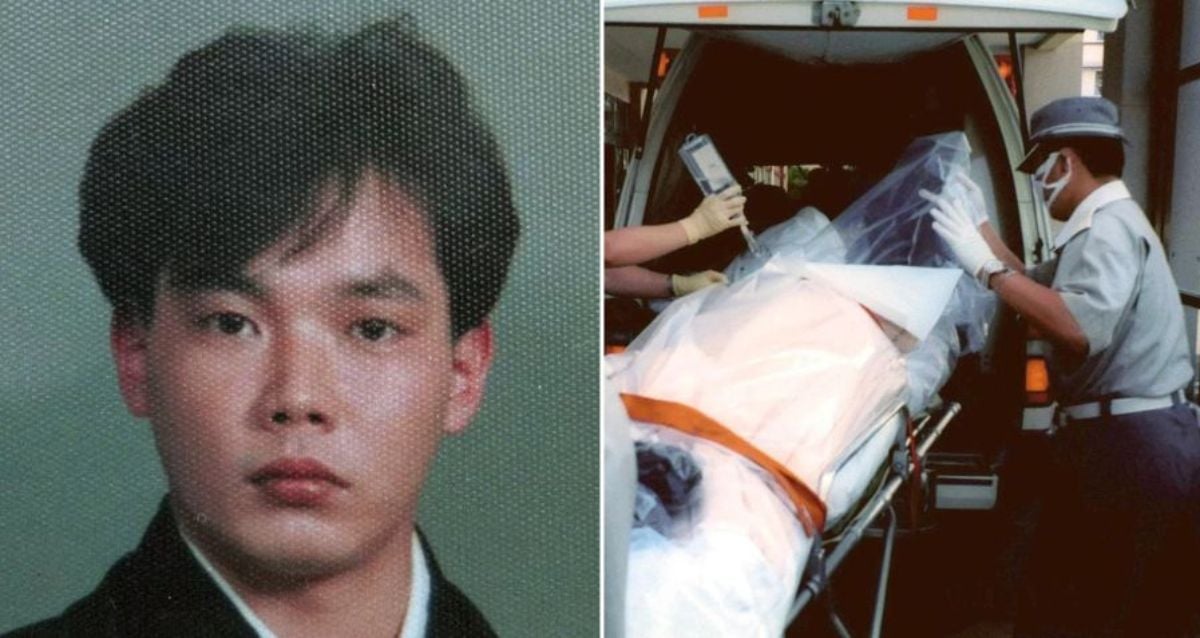
The Tokai nuclear accident remains one of the most significant incidents in Japan's history, capturing global attention and sparking debates about nuclear safety. This event has shaped policies, regulations, and public perception of nuclear energy worldwide. Understanding the causes, consequences, and lessons learned is crucial for ensuring a safer future in nuclear energy operations.
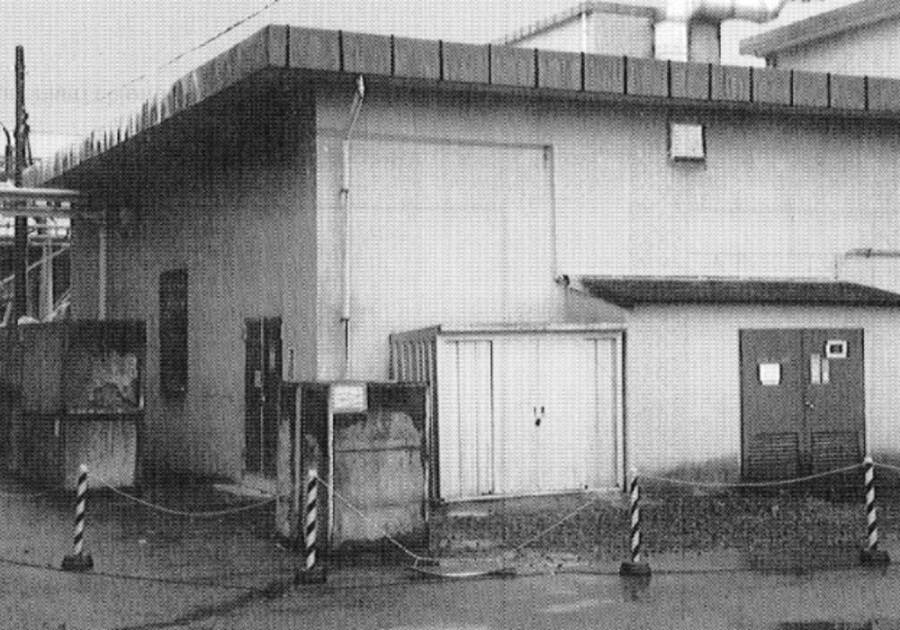
The Tokai nuclear accident occurred in 1999, marking a turning point in Japan's approach to nuclear safety. The incident involved a criticality accident at the JCO nuclear fuel processing facility in Tokai-mura, Ibaraki Prefecture. This event highlighted the dangers of improper safety protocols and inadequate training in nuclear facilities.
This article delves into the details of the Tokai nuclear accident, exploring its causes, impact, and the measures taken to prevent similar incidents in the future. By understanding the complexities surrounding this event, we can appreciate the importance of stringent safety standards in nuclear operations.
Read also:Sullivanking Mortuary Obituaries A Comprehensive Guide To Honoring Lives
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Tokai Nuclear Accident
- Background of JCO Facility
- Causes of the Accident
- Impact on Local Communities
- Health Effects and Radiation Exposure
- Improvements in Nuclear Safety Measures
- Regulatory Changes Post-Accident
- Global Response and Lessons Learned
- Public Perception and Trust Issues
- Future Directions in Nuclear Energy
Introduction to Tokai Nuclear Accident
The Tokai nuclear accident occurred on September 30, 1999, at the JCO nuclear fuel processing plant located in Tokai-mura, Japan. This criticality accident was caused by the improper handling of enriched uranium solutions, leading to an uncontrolled chain reaction. The incident highlighted significant lapses in safety protocols and training within the nuclear industry.
Despite its relatively small scale compared to major disasters like Chernobyl or Fukushima, the Tokai nuclear accident had far-reaching implications for nuclear safety standards. It prompted a reevaluation of safety practices and regulatory frameworks globally, emphasizing the importance of rigorous training and adherence to safety protocols.
Understanding the root causes of the accident and its consequences is essential for preventing similar incidents in the future. This section explores the timeline of events and the immediate response to the accident, shedding light on the complexities involved in nuclear safety management.
Background of JCO Facility
History of JCO
JCO Co., Ltd., established in 1972, was a subsidiary of Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd. The company specialized in nuclear fuel processing and conversion services. The Tokai-mura facility was designed to produce uranium hexafluoride (UF6) for use in nuclear reactors.
Prior to the accident, the JCO facility had a reputation for efficiency and innovation in nuclear fuel processing. However, the lack of stringent safety protocols and inadequate employee training became glaringly apparent following the incident.
Facility Operations
The facility's primary function was to convert uranium oxide (UO2) into uranium hexafluoride (UF6), a critical step in the nuclear fuel cycle. This process involved dissolving uranium oxide in nitric acid and then converting it into uranium tetrafluoride (UF4) before further processing.
Read also:How Old Is Kaleb From Shriners Hospital A Heartwarming Journey Through His Life
- Uranium oxide dissolution
- Conversion to uranium tetrafluoride
- Final production of uranium hexafluoride
The accident occurred during the dissolution process when workers mistakenly used a stainless-steel bucket to mix uranium oxide with nitric acid, exceeding the critical mass limit and triggering a chain reaction.
Causes of the Accident
The primary cause of the Tokai nuclear accident was human error exacerbated by inadequate safety protocols. The workers involved in the incident violated established procedures by mixing uranium oxide in a stainless-steel bucket instead of using the designated precipitation tank, which was designed to prevent criticality.
Key factors contributing to the accident include:
- Inadequate training for employees
- Failure to adhere to established safety protocols
- Poor communication between staff and management
- Insufficient regulatory oversight
These lapses underscore the importance of robust safety measures and continuous training programs in nuclear facilities. The incident serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of complacency in nuclear operations.
Impact on Local Communities
Immediate Evacuation
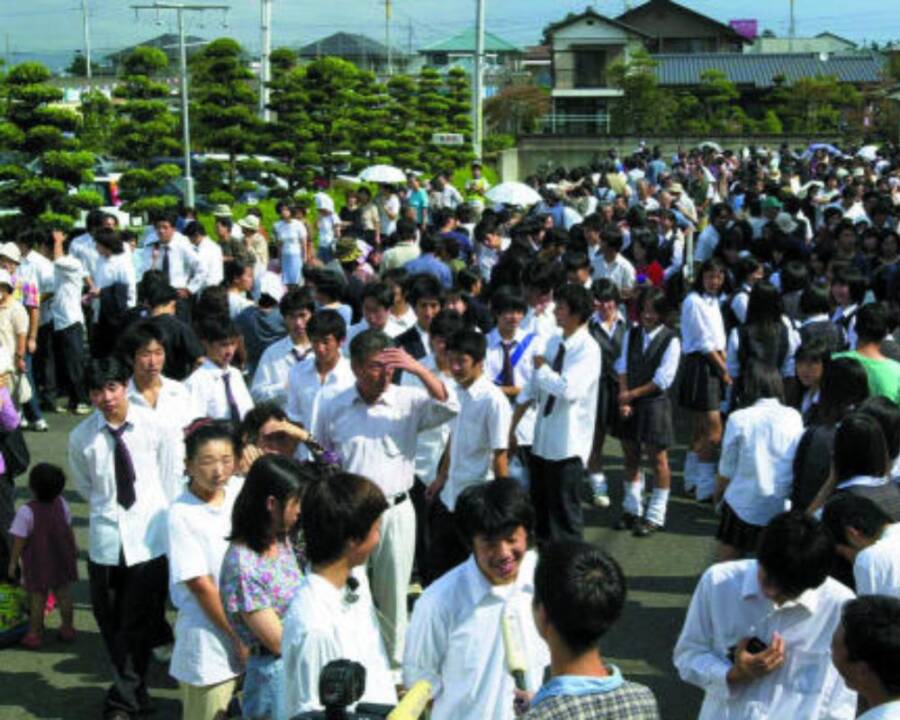
Following the accident, authorities quickly evacuated approximately 160 residents living within a 350-meter radius of the facility. The evacuation zone was expanded to include 310 additional households as a precautionary measure. Although no immediate fatalities were reported, the psychological impact on residents was significant.
Long-Term Effects
The accident's long-term effects on local communities included economic disruptions, social anxiety, and a loss of trust in nuclear energy. Many residents experienced financial hardships due to the closure of businesses in the area and the stigma associated with living near a nuclear facility.
Data from the World Nuclear Association indicates that the accident resulted in a temporary shutdown of several nuclear facilities in Japan, leading to increased reliance on fossil fuels and higher energy costs.
Health Effects and Radiation Exposure
While the Tokai nuclear accident did not result in widespread radiation exposure, three workers at the facility were exposed to lethal doses of radiation. Two of the workers eventually succumbed to radiation sickness, highlighting the dangers of criticality accidents.
Studies conducted by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) revealed that radiation levels in the surrounding area were below harmful thresholds for the general population. However, the psychological impact on residents and workers cannot be overlooked, as fear of radiation exposure persisted long after the incident.
Improvements in Nuclear Safety Measures
In response to the Tokai nuclear accident, significant improvements were made in nuclear safety measures worldwide. These enhancements include:
- Stricter safety protocols and training programs
- Enhanced regulatory oversight and compliance
- Development of advanced monitoring systems
- Improved communication between staff and management
These measures have contributed to a safer nuclear energy sector, reducing the likelihood of similar accidents in the future. The IAEA continues to play a vital role in promoting global nuclear safety standards and best practices.
Regulatory Changes Post-Accident
Revisions to Safety Standards
Following the accident, Japan's government implemented sweeping regulatory changes to enhance nuclear safety. The Nuclear Safety Commission (NSC) introduced stricter guidelines for facility design, operation, and emergency preparedness.
International Collaboration
The Tokai nuclear accident prompted increased international collaboration on nuclear safety issues. Countries shared best practices and lessons learned, fostering a more unified approach to nuclear safety worldwide.
According to the Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA), international cooperation has led to significant improvements in nuclear safety standards, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing public confidence in nuclear energy.
Global Response and Lessons Learned
The global response to the Tokai nuclear accident emphasized the importance of transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement in nuclear safety. Countries around the world conducted reviews of their own nuclear facilities, identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing corrective actions.
Key lessons learned from the accident include:
- The critical importance of adhering to safety protocols
- The necessity of comprehensive employee training programs
- The value of robust regulatory oversight
These lessons have shaped modern nuclear safety practices, ensuring a safer and more reliable energy source for future generations.
Public Perception and Trust Issues
The Tokai nuclear accident significantly impacted public perception of nuclear energy in Japan and globally. Many people developed a fear of nuclear power, associating it with catastrophic risks and potential health hazards.
Restoring public trust in nuclear energy requires transparent communication, rigorous safety standards, and proactive engagement with communities. Governments and industry leaders must work together to address concerns and demonstrate the safety and reliability of nuclear energy.
Future Directions in Nuclear Energy
The future of nuclear energy depends on continued advancements in technology, safety, and public acceptance. Innovations in reactor design, fuel recycling, and waste management offer promising solutions for addressing current challenges in the nuclear energy sector.
As the world seeks to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, nuclear energy remains a vital component of the global energy mix. By learning from past incidents like the Tokai nuclear accident, we can ensure a safer and more sustainable future for nuclear energy.
Conclusion
The Tokai nuclear accident serves as a sobering reminder of the importance of safety in nuclear operations. By understanding the causes and consequences of this incident, we can implement measures to prevent similar accidents in the future. The lessons learned from the accident have significantly contributed to advancements in nuclear safety standards and regulatory frameworks worldwide.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Your feedback is invaluable in fostering a deeper understanding of nuclear safety and promoting a safer energy future. For more informative articles on nuclear energy and related topics, explore our website and stay updated on the latest developments in this critical field.